Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is more common problem than you might think. Nearly 2.5 billion people are projected to have some degree of hearing loss by 2050, and over 1 billion young adults are at risk of permanent, avoidable hearing loss due to unsafe listening practices. Hearing Loss has three different types:
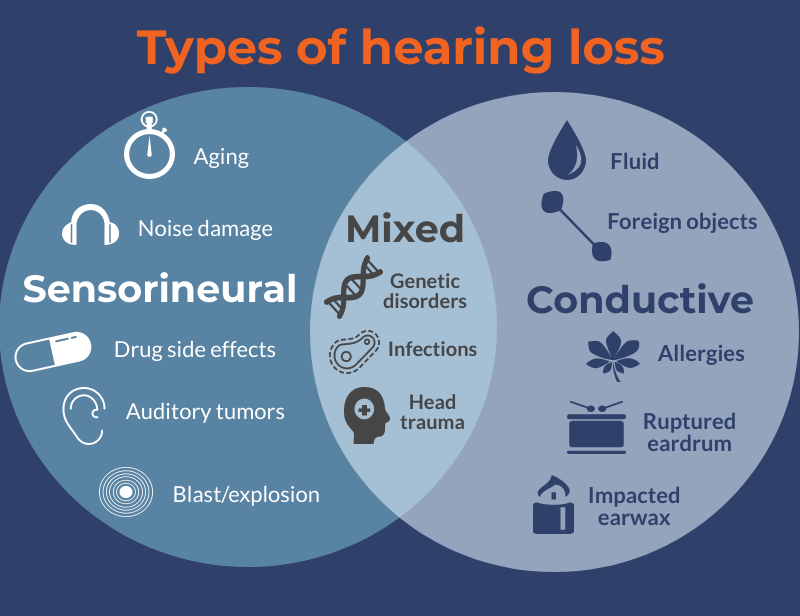
Conductive Loss :
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss results from a problem with the outer or middle ear. This includes your ear canal, eardrum or the ear bones known as the ossicles. A blockage interferes with how sound gets conducted through the ear, making sound levels seem lower. Some causes of conductive hearing loss include fluid in the middle ears resulting from a cold or allergies, poor Eustachian tube function, ear infections, or a perforated eardrum. Also, impacted wax or the presence of a foreign body can result in a conductive loss.
Sensorineural Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss results in damage to the inner ear, the nerve pathway from the inner ear to the brain or both. The most common type is caused by the outer hair cell not functioning properly. Some causes of sensorineural hearing loss are birth injury, disease, or drugs that are toxic to the auditory system. Sensorineural hearing loss may also occur as a result of noise exposure, head trauma, viruses( Sudden Loss), and the aging process. This person has trouble hearing clearly and understanding speech. Sensorineural hearing loss is a permanent loss and cannot be treated surgically or medically.
Mixed Loss
Mixed Hearing loss results when a person has a combination of a conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. In these cases there may be damage in the outer ear or middle ear as well as the cochlea or auditory nerve.